How to Use Device Query in Intune
Device Query will help you to collect the n-demand device information quickly. Device query runs in a real-time and will provide real-time data from the device.
Prerequisites
Microsoft Intune Advanced Analytics should be activated on Tenant You should have below license to use Device Query feature.
- Intune Advanced Analytics Add-on.
- Microsoft Intune Suite.
To use Device query on a device, the device must be enrolled in Endpoint Analytics.
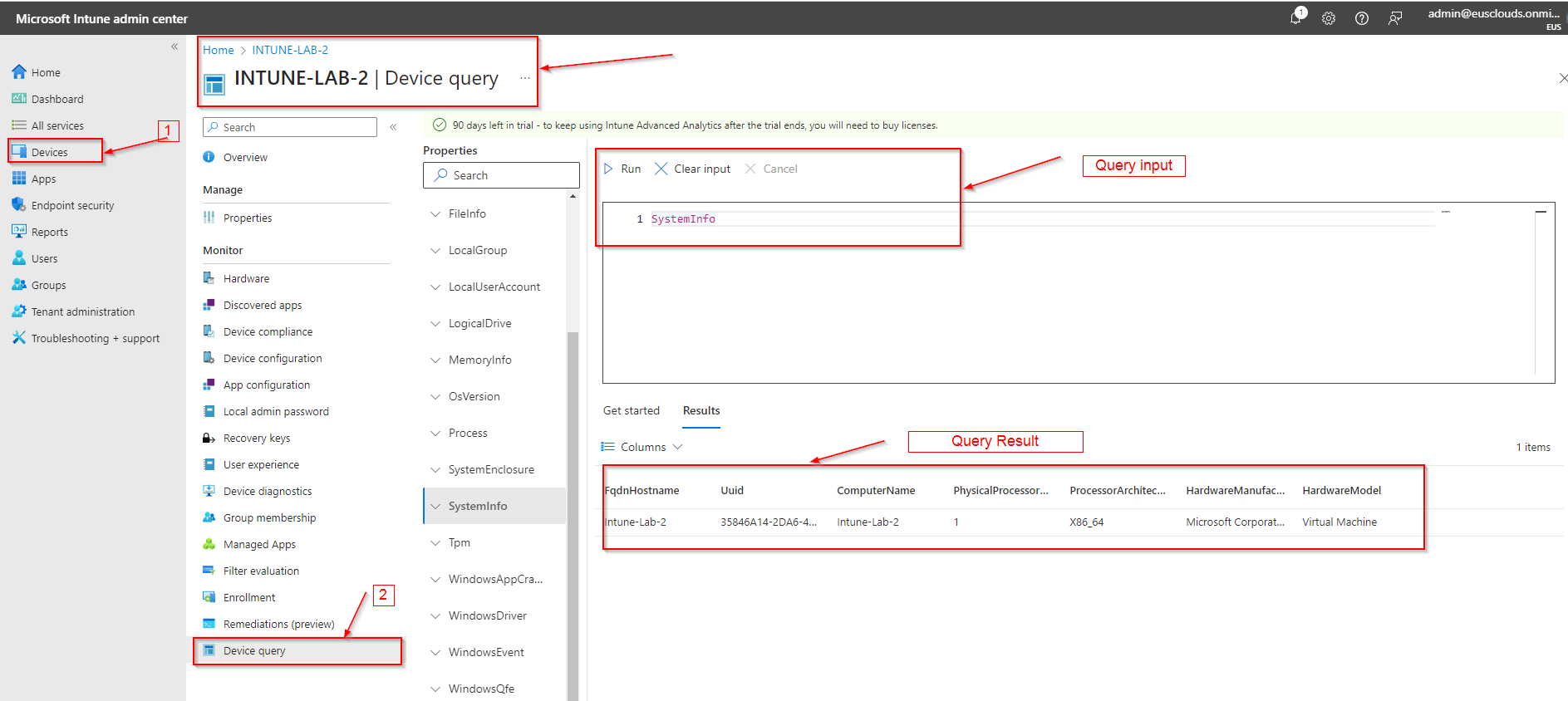
To use Device Query, Go to Devices and then All Devices then search device then click on Device Query as showing in below screen.
Supported Properties
Device query supports the following entities. To learn more about what properties are supported for each entity, see Intune Data Platform Schema.
BiosInfo
Certificate
Cpu
DiskDrive
EncryptableVolume
FileInfo
LocalGroup
LocalUserAccount
LogicalDrive
MemoryInfo
OsVersion
Process
SystemEnclosure
SystemInfo
Tpm
WindowsAppCrashEvent
WindowsDriver
WindowsEvent
WindowsQfe
WindowsRegistry
WindowsService
Table Operators
Table operators can be used filter, summarize, and transform data streams. Currently the following operators are supported:
| Operators | Description |
| count | Returns a table with a single record containing the number of records |
| distinct | Produces a table with the distinct combination of the provided columns of the input table |
| join | Merge the rows of two tables to form a new table by matching row for the same device |
| order by | Sort the rows of the input table into order by one or more columns |
| project | Select the columns to include, rename or drop, and insert new computed columns |
| take | Return up to the specified number of rows |
| top | Returns the first N records sorted by the specified columns |
| where | Filters a table to the subset of rows that satisfy a predicate |
Scalar operators
The following table summarizes operators:
| Operators | Description | Example |
| == | Equal | 1 == 1, ‘aBc’ == ‘AbC’ |
| != | Not Equal | 1 != 2, ‘abc’ != ‘abcd’ |
| < | Less | 1 < 2, ‘abc’ < ‘DEF’ |
| > | Greater | 2 > 1, ‘xyz’ > ‘XYZ’ |
| <= | Less or Equal | 1 <= 2, ‘abc’ <= ‘abc’ |
| >= | Greater or Equal | 2 >= 1, ‘abc’ >= ‘ABC’ |
| + | Add | 2 + 1, now() + 1d |
| – | Subtract | 2 – 1, now() – 1h |
| * | Multiply | 2 * 2 |
| / | Divide | 02-Jan |
| % | Modulo | 2 % 1 |
| like | Left Hand Side (LHS) contains a match for Right Hand Side (RHS) | ‘abc’ like ‘%B%’ |
| !like | LHS doesn’t contain a match for RHS | ‘abc’ !like ‘_d_’ |
| contains | RHS occurs as a subsequence of LHS | ‘abc’ contains ‘b’ |
| !contains | RHS doesn’t occur in LHS | ‘team’ !contains ‘i’ |
| startswith | RHS is an initial subsequence of LHS | ‘team’ startswith ‘tea’ |
| !startswith | RHS isn’t an initial subsequence of LHS | ‘abc’ !startswith ‘bc’ |
| endswith | RHS is a closing subsequence of LHS | ‘abc’ endswith ‘bc’ |
| !endswith | RHS isn’t a closing subsequence of LHS | ‘abc’ !endswith ‘a’ |
| and | True if and only if RHS and LHS are true | (1 == 1) and (2 == 2) |
| or | True if and only if RHS or LHS is true | (1 == 1) or (1 == 2) |
Aggregation functions
Aggregation functions can be used with the summarize table operator to calculate summarized values. Currently the following aggregation functions are supported:
| Function | Description |
| avg() | Returns the average of the values across the group |
| count() | Returns a count of the records per summarization group |
| countif() | Returns a count of rows for which Predicate evaluates to true |
| dcount() | Returns the number of distinct values in the group |
| max() | Returns the maximum value across the group |
| maxif() | Starting in version 2107, you can use maxif with the summarize table operator. |
| Returns the maximum value across the group for which Predicate evaluates to true. | |
| min() | Returns the minimum value across the group |
| minif() | Starting in version 2107, you can use minif with the summarize table operator. |
| Returns the minimum value across the group for which Predicate evaluates to true. | |
| percentile() | Returns an estimate for the specified nearest-rank percentile of the population defined by Expr |
| sum() | Returns the sum of the values across the group |
| sumif() | Returns a sum of Expr for which Predicate evaluates to true |
Scalar functions
Scalar functions can be used in expressions. Currently the following scalar functions are supported:
| Function | Description |
| ago() | Subtracts the given timespan from the current UTC clock time |
| bin() | Rounds values down to many datetime multiple of a given bin size |
| case() | Evaluates a list of predicates and returns the first result expression whose predicate is satisfied |
| datetime_add() | Calculates a new datetime from a specified datepart multiplied by a specified amount, added to a specified datetime |
| datetime_diff() | Calculates the difference between two date time values |
| iif() | Evaluates the first argument and returns the value of either the second or third arguments depending on whether the predicate evaluated to true (second) or false (third) |
| indexof() | Function reports the zero-based index of the first occurrence of a specified string within input string |
| isnotnull() | Evaluates its sole argument and returns a Boolean value indicating if the argument evaluates to a non-null value |
| isnull() | Evaluates its sole argument and returns a Boolean value indicating if the argument evaluates to a null value |
| now() | Returns the current UTC clock time |
| strcat() | Concatenates between 1 and 64 arguments |
| strlen() | Returns the length, in characters, of the input string |
| substring() | Extracts a substring from a source string starting from some index to the end of the string |
| tostring() | Converts input to a string representation |
